can lialh4 reduce carboxylic acids Carboxylic lialh4 reduction lithium hydride aluminum acids reducing acid alcohol aldehyde mechanism agent reaction reduces lialh pulled
The reduction of carbonyl compounds is a fundamental process in the field of organic chemistry. It involves the addition of hydride ions to the carbon-oxygen double bond present in aldehydes, ketones, esters, carboxylic acids, and acid chlorides. One of the most commonly used reagents for this purpose is lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4). Another reagent that is often employed is sodium borohydride (NaBH4). These reagents play a crucial role in the synthesis of various organic compounds and are widely utilized in laboratory settings for their powerful reducing properties.
LiAlH4 Carbonyl Reduction Mechanism
 The reduction mechanism of carbonyl compounds using LiAlH4 involves a two-step process. In the first step, LiAlH4 acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon of the carbonyl group, forming an intermediate alkoxide species. This step is followed by protonation, where the negatively charged alkoxide species is neutralized by the addition of a proton (H+). This results in the formation of an alcohol as the final product.
The reduction mechanism of carbonyl compounds using LiAlH4 involves a two-step process. In the first step, LiAlH4 acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon of the carbonyl group, forming an intermediate alkoxide species. This step is followed by protonation, where the negatively charged alkoxide species is neutralized by the addition of a proton (H+). This results in the formation of an alcohol as the final product.
LiAlH4 Reducing Capability
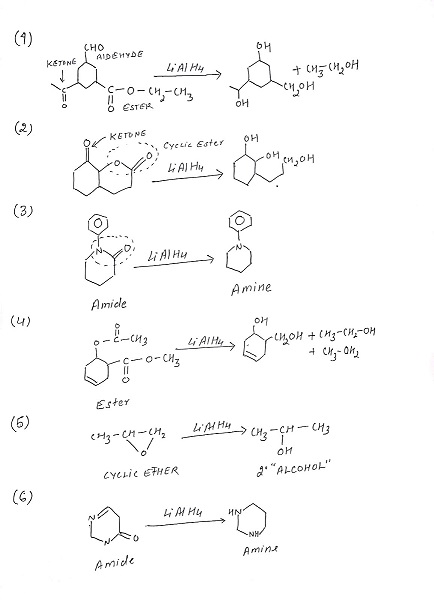 LiAlH4 is a highly versatile reducing agent and can effectively reduce a wide range of functional groups in addition to carbonyl compounds. It can reduce carboxylic acids, acid chlorides, esters, and even certain functional groups like nitriles, nitro compounds, and azides. This makes LiAlH4 an invaluable tool in organic synthesis, as it allows for the selective reduction of specific functional groups while leaving others untouched. However, it is worth noting that LiAlH4 is a very strong reducing agent and must be handled with utmost care due to its reactivity.
LiAlH4 is a highly versatile reducing agent and can effectively reduce a wide range of functional groups in addition to carbonyl compounds. It can reduce carboxylic acids, acid chlorides, esters, and even certain functional groups like nitriles, nitro compounds, and azides. This makes LiAlH4 an invaluable tool in organic synthesis, as it allows for the selective reduction of specific functional groups while leaving others untouched. However, it is worth noting that LiAlH4 is a very strong reducing agent and must be handled with utmost care due to its reactivity.
In conclusion, LiAlH4 and NaBH4 are powerful reagents utilized for the reduction of carbonyl compounds in organic chemistry. These reagents enable the synthesis of a wide range of organic compounds by selectively reducing the carbonyl group while leaving other functional groups intact. They offer great versatility and have found widespread use in laboratory settings. Understanding the mechanism and capabilities of these reagents is essential for any professional in the field of organic synthesis.
If you are searching about LiAlH4 and NaBH4 Carbonyl Reduction Mechanism - Chemistry Steps (2022) you’ve visit to the right web. We have 5 Images about LiAlH4 and NaBH4 Carbonyl Reduction Mechanism - Chemistry Steps (2022) like Image result for lialh4 | Organic chemistry, Chemistry, Organic, Reduction of carboxylic acids to primary alcohols using LiAlH4 – Master and also Image result for lialh4 | Organic chemistry, Chemistry, Organic. Here it is:
LiAlH4 And NaBH4 Carbonyl Reduction Mechanism - Chemistry Steps (2022)
 fyrick.comWelcome To Chem Zipper.com……: What Are The Groups That LiAlH4 Can
fyrick.comWelcome To Chem Zipper.com……: What Are The Groups That LiAlH4 Can
 www.chemzipper.comlialh4 reduce groups cannot important notes
www.chemzipper.comlialh4 reduce groups cannot important notes
Lithium Aluminum Hydride As A Reducing Agent | Student Doctor Network
 forums.studentdoctor.netcarboxylic lialh4 reduction lithium hydride aluminum acids reducing acid alcohol aldehyde mechanism agent reaction reduces lialh pulled
forums.studentdoctor.netcarboxylic lialh4 reduction lithium hydride aluminum acids reducing acid alcohol aldehyde mechanism agent reaction reduces lialh pulled
Image Result For Lialh4 | Organic Chemistry, Chemistry, Organic
 www.pinterest.com.mxlialh4 lah lithium hydride organic nabh4 mechanism ester riduzione reactions mechanisms composti litio chemia lialh nh2 amide
www.pinterest.com.mxlialh4 lah lithium hydride organic nabh4 mechanism ester riduzione reactions mechanisms composti litio chemia lialh nh2 amide
Reduction Of Carboxylic Acids To Primary Alcohols Using LiAlH4 – Master
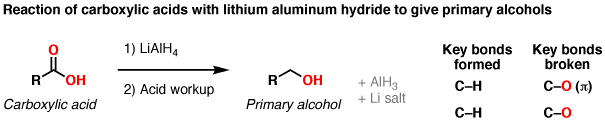 www.masterorganicchemistry.comWelcome to chem zipper.com……: what are the groups that lialh4 can. Image result for lialh4. Reduction of carboxylic acids to primary alcohols using lialh4 – master
www.masterorganicchemistry.comWelcome to chem zipper.com……: what are the groups that lialh4 can. Image result for lialh4. Reduction of carboxylic acids to primary alcohols using lialh4 – master